Pontiac Trans Am Firebird V8 2000HP BURNOUT SOUND ACCELERATION
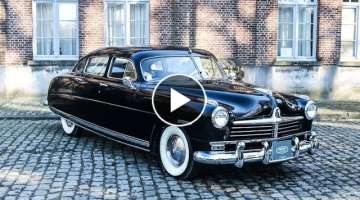
The 1973 Pontiac Firebird wore styling introduced in 1970 and would continue through 1981. The Firebird was introduced in 1967, and its first generation of styling continued through 1969. The second generation was delayed until late-February of 1970 due to engineering and tooling issues, so leftover 1969 models were listed in early Pontiac literature without a model-year identification and the 1970 models are popularly referred to as a 1970½ model. The 'Coke bottle' styling of the '1st Gen' was replaced by more rounded body lines of the '2nd Gen' accented by swoopy curves, a large B-pillar, and a lip on the trunk lid.
American V-8 high-performance cars were nearly extinct by the early 1970s, but the Chevy Camaro and Pontiac Firebird soldiered on, enjoying fast-growing popularity due to their potent engines, bold styling, and exceptional handling. A UAW strike at the GM assembly plant in Norwood in 1972 nearly convinced management to end production of the Firebird and the similar F-body Camaro. When production resumed, at least 1,100 incomplete Camaros had to be scrapped due to not complying with the new 1973 federal safety standards. Additionally, management was under pressure to comply with difficult new regulations for safety, fuel economy, and emissions.
For 1973, trim levels included the 'base' Firebird, Firebird Esprit, Firebird Formula, and Firebird Trans Am. The Esprit had a higher level of trim and accouterments than the base, with a custom interior, twin body-color mirrors, African cross-fire mahogany dash, and concealed windshield wipers. The Formula had a unique twin-scoop hood, a heavy-duty suspension, a black textured grille, dual exhaust, F70-14 tires, a custom cushion steering wheel, and items installed on the 'base' and Formula.
The 1973 Pontiac Firebird Trans Am wore aerodynamically styled outside mirrors with the left-hand side being remote-controlled, heavy-duty shock absorbers and springs, front and rear stabilizer bars, front and rear spoilers (the rear was a full-width deck spoiler), front fender air extractors shaker hood, side air extractors, concealed wipers, power front disc brakes and steering, 7-inch wide 15-inch diameter Rally II wheels with trim rings, F60-15 raised white letter tires, dual body-color mirrors with the left-hand being remote-controlled, Safe-T-Track differential, wheel opening flares, dual exhaust with chrome extensions, and front air dams. The interiors housed a Rally gauge cluster with a tachometer and clock, engine-turned dash inserts, a Formula steering wheel, bucket seats, carpeting, and vinyl upholstery.
New for 1973 was the addition of the 'chicken' graphics treatment for the hood.
The standard engine powering the Trans Am was a 455 cubic-inch V8 with 8.0:1 compression, a four-barrel carburetor, and 250 horsepower at 4,000 RPM. The base transmission was either a four-speed manual or the Turbo-Hydramatic.
Pontiac engineers led by Special Projects Engineer Herb Adams and Senior Project Leaders Skip McCully and Tom Nell designed the Super Duty 455 engine and somehow managed to get it approved for sale as a factory option for 1973. Equally impressive was the 'Super Duty' name which vividly recalled the all-out Pontiac performers of the early 1960s that ruled drag strips, NASCAR ovals, and street racing. During the pervasive anti-performance stigma at General Motors, and the entire society of the era, the 'Super Duty' name and the high-performance 455 CID V8 were allowed to exist.
The Super Duty 455 engine received a stronger block with four-bolt mains, aluminum pistons, high-flow heads and manifolds, forged-steel connecting rods, a single Rochester Quadrajet 800-CFM four-barrel carburetor, and a Ram Air III camshaft. The engine was conservatively rated at 290 (SAE net) horsepower. Built using leftover components from Pontiac's 366 NASCAR engine, the SD-455 was capable of producing over 540 horsepower but was toned down to satisfy the EPA and comply with GM's strict horsepower policy which required all GM vehicles to hold the HP under 300.
In period road tests, the 455 Super Duty Firebirds with a Turbo-Hydramatic 400 (the standard gear ratio for the Super Duty model was 3.421) posted 13-second quarter-miles at over 103 mph through the traps and accelerated from 0 to 60 in 5.4 seconds. It had the highest top speed, lowest zero-to-sixty mph, and quickest quarter-mile times compared to the Buick Special GS, Dodge Charger, AMC Javelin, and the Mustang Mach 1.
The 1974 SD-455 Firebird would continue unchanged except for the new front-end design. Most of the 1001 SD-455 Firebirds were Trans Am models, and 252 Super Duty 455-powered Pontiacs were built for 1973, nearly all were Trans Ams. Of those, 72 were equipped with a four-speed manual transmission and 180 with the automatic.
Pontiac produced 14,096 examples of the 'base' Firebird for 1973, 17,249 of the Firebird Esprit, 10,166 of the Firebird Formula, and 4,802 of the Trans Am. The base Firebird had a factory price of $2,890, the Firebird Esprit listed at $3,250, the Firebird Formula at $3,275, and the Trans Am topped the list at $4,200.
In comparison, the total production of the 1973 Chevy Camaro was 89,988 units, including 32,327 LT, 16,133 RS, and 11,574 Z/28s. The Z/28 Camaro came equipped with the 350 CID V8 equipped with a new low-restriction air cleaner and rated at 245 hp.
As the years progressed, performance continued to decline as power dropped and weight increased due to emissions and fuel-economy restrictions, and safety equipment installed to comply with the new legislation. All-new styling was introduced in 1982, and the F-body car became lighter, and its design was heavily influenced by aerodynamics.
VIDEO
Facebook Comments